当MongoDB遇见Spark
传统Spark生态系统
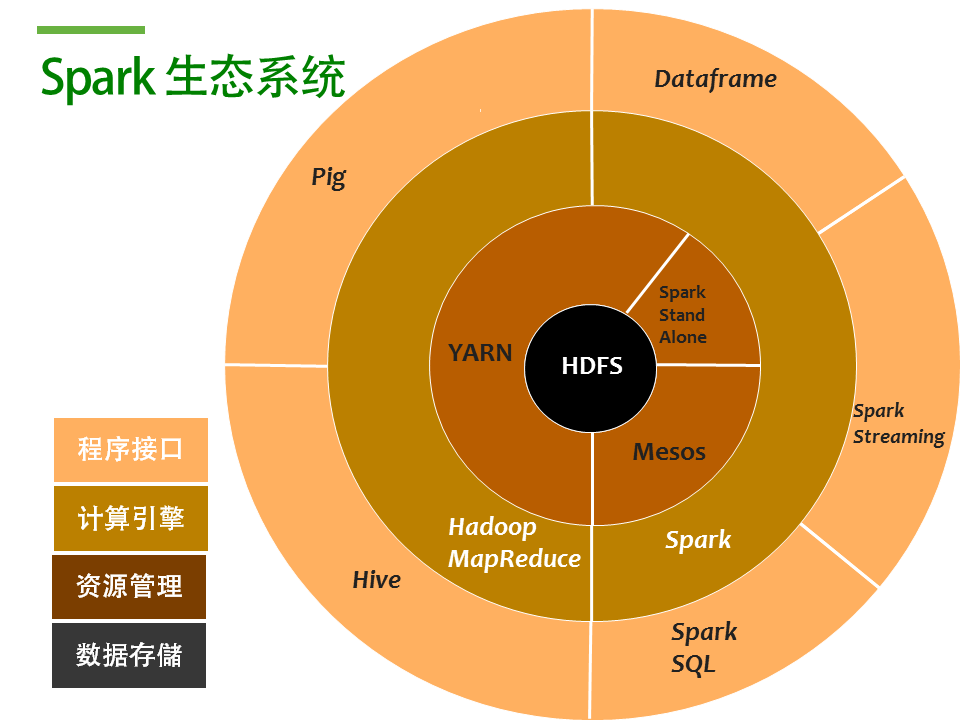
那么Mongodb作为一个database, 可以担任什么样的角色呢? 就是数据存储这部分, 也就是图中的黑色圈圈HDFS的部分, 如下图
用MongoDB替换HDFS后的Spark生态系统
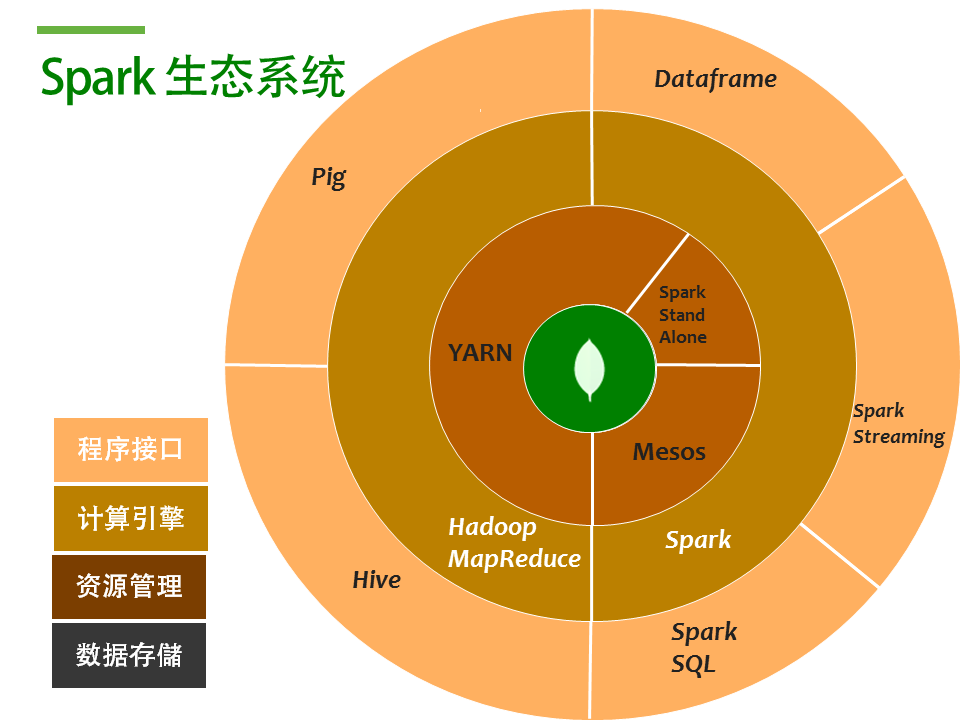
为什么要用MongoDB替换HDFS
- 存储方式上, HDFS以文件为单位,每个文件64MB~128MB不等, 而MongoDB作为文档数据库则表现得更加细颗粒化
- MongoDB支持HDFS所没有的索引的概念, 所以在读取上更加快
MongoDB支持的增删改功能比HDFS更加易于修改写入后
HDFS的响应级别为分钟, 而MongoDB通常是毫秒级别
- 如果现有数据库已经是MongoDB的话, 那就不用再转存一份到HDFS上了
- 可以利用MongoDB强大的Aggregate做数据的筛选或预处理
MongoDB Spark Connector介绍
- 支持读取和写入,即可以将计算后的结果写入MongoDB
- 将查询拆分为n个子任务, 如Connector会将一次match,拆分为多个子任务交给spark来处理, 减少数据的全量读取
MongoDB Spark 示例代码
计算用类型Type=1的message字符数并按userid进行分组
开发Maven dependency配置
这里用的是mongo-spark-connector_2.11 的2.0.0版本和spark的spark-core_2.11的2.0.2版本
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mongodb.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>mongo-spark-connector_2.11</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-core_2.11</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
</dependency>
示例代码
import com.mongodb.spark._
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
import org.bson._
val conf = new SparkConf()
.setMaster("local")
.setAppName("Mingdao-Score")
//同时还支持mongo驱动的readPreference配置, 可以只从secondary读取数据
.set("spark.mongodb.input.uri", "mongodb://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:27017,xxx.xxx.xxx:27017,xxx.xxx.xxx:27017/inputDB.collectionName")
.set("spark.mongodb.output.uri", "mongodb://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:27017,xxx.xxx.xxx:27017,xxx.xxx.xxx:27017/outputDB.collectionName")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
// 创建rdd
val originRDD = MongoSpark.load(sc)
// 构造查询
val dateQuery = new BsonDocument()
.append("$gte", new BsonDateTime(start.getTime))
.append("$lt", new BsonDateTime(end.getTime))
val matchQuery = new Document("$match", BsonDocument.parse("{\"type\":\"1\"}"))
// 构造Projection
val projection1 = new BsonDocument("$project", BsonDocument.parse("{\"userid\":\"$userid\",\"message\":\"$message\"}")
val aggregatedRDD = originRDD.withPipeline(Seq(matchQuery, projection1))
//比如计算用户的消息字符数
val rdd1 = aggregatedRDD.keyBy(x=>{
Map(
"userid" -> x.get("userid")
)
})
val rdd2 = rdd1.groupByKey.map(t=>{
(t._1, t._2.map(x => {
x.getString("message").length
}).sum)
})
rdd2.collect().foreach(x=>{
println(x)
})
//保持统计结果至MongoDB outputurl 所指定的数据库
MongoSpark.save(rdd2)
总结
MongoDB Connector 的文档只有基础的示例代码, 具体详情需要看GitHub中的example和部分源码
参考链接
mongo-spark/examples/src/test/python/introduction.py
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
#
# Copyright 2016 MongoDB, Inc.
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# To run this example use:
# ./bin/spark-submit --master "local[4]" \
# --conf "spark.mongodb.input.uri=mongodb://127.0.0.1/test.coll?readPreference=primaryPreferred" \
# --conf "spark.mongodb.output.uri=mongodb://127.0.0.1/test.coll" \
# --packages org.mongodb.spark:mongo-spark-connector_2.11:2.0.0 \
# introduction.py
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
if __name__ == "__main__":
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("Python Spark SQL basic example").getOrCreate()
logger = spark._jvm.org.apache.log4j
logger.LogManager.getRootLogger().setLevel(logger.Level.FATAL)
# Save some data
characters = spark.createDataFrame([("Bilbo Baggins", 50), ("Gandalf", 1000), ("Thorin", 195), ("Balin", 178), ("Kili", 77), ("Dwalin", 169), ("Oin", 167), ("Gloin", 158), ("Fili", 82), ("Bombur", None)], ["name", "age"])
characters.write.format("com.mongodb.spark.sql").mode("overwrite").save()
# print the schema
print("Schema:")
characters.printSchema()
# read from MongoDB collection
df = spark.read.format("com.mongodb.spark.sql").load()
# SQL
df.registerTempTable("temp")
centenarians = spark.sql("SELECT name, age FROM temp WHERE age >= 100")
print("Centenarians:")
centenarians.show()