Spiders
Spider类定义了如何爬取某个(或某些)网站。包括了爬取的动作(例如:是否跟进链接)以及如何从网页的内容中提取结构化数据(爬取item)。 换句话说,Spider就是定义爬取的动作及分析某个网页(或者是有些网页)的地方。
Spider
class scrapy.spider.Spider
Spider是最简单的spider。每个spider必须继承自该类。Spider并没有提供什么特殊的功能。其仅仅请求给定的 start_urls/start_requests,并根据返回的结果调用spider的parse方法。
name
定义spider名字的字符串。
例如,如果spider爬取 mywebsite.com ,该spider通常会被命名为 mywebsite
allowed_domains
可选。包含了spider允许爬取的域名(domain)列表(list)
start_urls
初始URL列表。当没有制定特定的URL时,spider将从该列表中开始进行爬取。
start_requests()
当spider启动爬取并且未指定start_urls时,该方法被调用。
如果您想要修改最初爬取某个网站
例如,如果您需要在启动时以POST登录某个网站,你可以这么写:
class MySpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'myspider' def start_requests(self): return [scrapy.FormRequest("http://www.example.com/login", formdata={'user': 'john', 'pass': 'secret'}, callback=self.logged_in)] def logged_in(self, response): # here you would extract links to follow and return Requests for # each of them, with another callback passparse(response)
当请求url返回网页没有指定回调函数时,默认下载回调方法。
参数:
response (Response) – 返回网页信息的responselog(message[, level, component])
使用 scrapy.log.msg() 方法记录(log)message。 更多数据请参见 Logging
Spider样例
让我们来看一个例子:
import scrapy
class MySpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'example.com'
allowed_domains = ['example.com']
start_urls = [
'http://www.example.com/1.html',
'http://www.example.com/2.html',
'http://www.example.com/3.html',
]
def parse(self, response):
self.log('A response from %s just arrived!' % response.url)
另一个在单个回调函数中返回多个Request以及Item的例子:
import scrapy
from myproject.items import MyItem
class MySpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'example.com'
allowed_domains = ['example.com']
start_urls = [
'http://www.example.com/1.html',
'http://www.example.com/2.html',
'http://www.example.com/3.html',
]
def parse(self, response):
sel = scrapy.Selector(response)
for h3 in response.xpath('//h3').extract():
yield MyItem(title=h3)
for url in response.xpath('//a/@href').extract():
yield scrapy.Request(url, callback=self.parse)
案例
腾讯招聘网翻页功能
import scrapy
from tutorial.items import RecruitItem
import re
class RecruitSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "tencent"
allowed_domains = ["hr.tencent.com"]
start_urls = [
"http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
]
def parse(self, response):
for sel in response.xpath('//*[@class="even"]'):
name = sel.xpath('./td[1]/a/text()').extract()[0]
detailLink = sel.xpath('./td[1]/a/@href').extract()[0]
catalog =None
if sel.xpath('./td[2]/text()'):
catalog = sel.xpath('./td[2]/text()').extract()[0]
recruitNumber = sel.xpath('./td[3]/text()').extract()[0]
workLocation = sel.xpath('./td[4]/text()').extract()[0]
publishTime = sel.xpath('./td[5]/text()').extract()[0]
#print name, detailLink, catalog,recruitNumber,workLocation,publishTime
item = RecruitItem()
item['name']=name.encode('utf-8')
item['detailLink']=detailLink.encode('utf-8')
if catalog:
item['catalog']=catalog.encode('utf-8')
item['recruitNumber']=recruitNumber.encode('utf-8')
item['workLocation']=workLocation.encode('utf-8')
item['publishTime']=publishTime.encode('utf-8')
yield item
nextFlag = response.xpath('//*[@id="next"]/@href')[0].extract()
if 'start' in nextFlag:
curpage = re.search('(\d+)',response.url).group(1)
page =int(curpage)+10
url = re.sub('\d+',str(page),response.url)
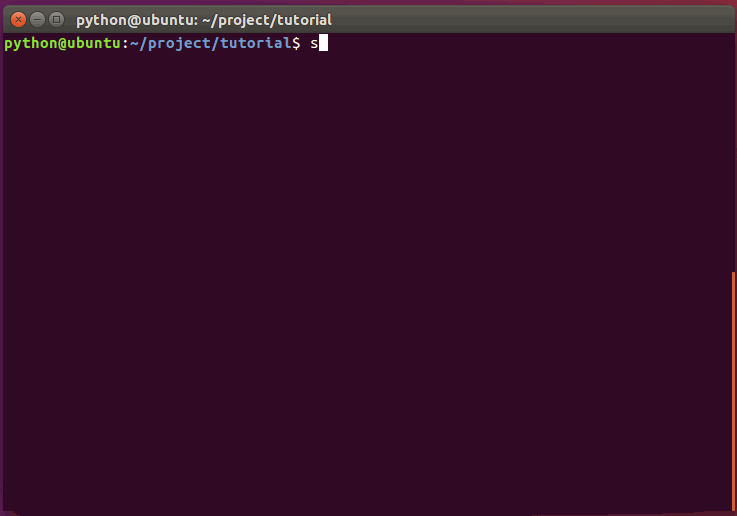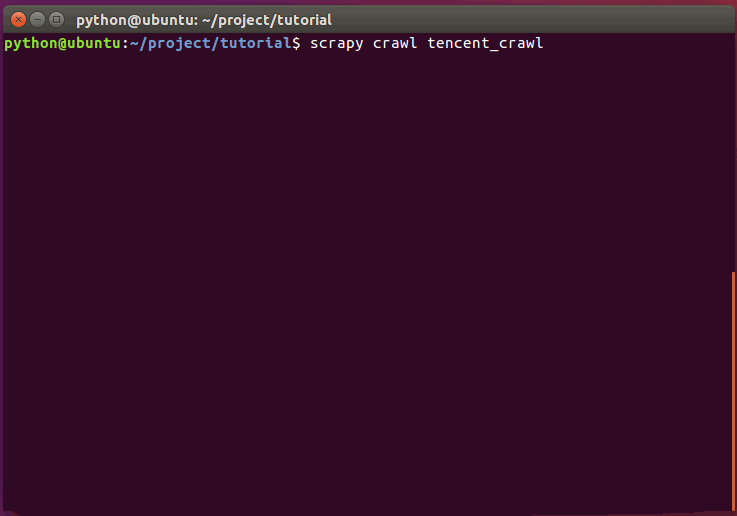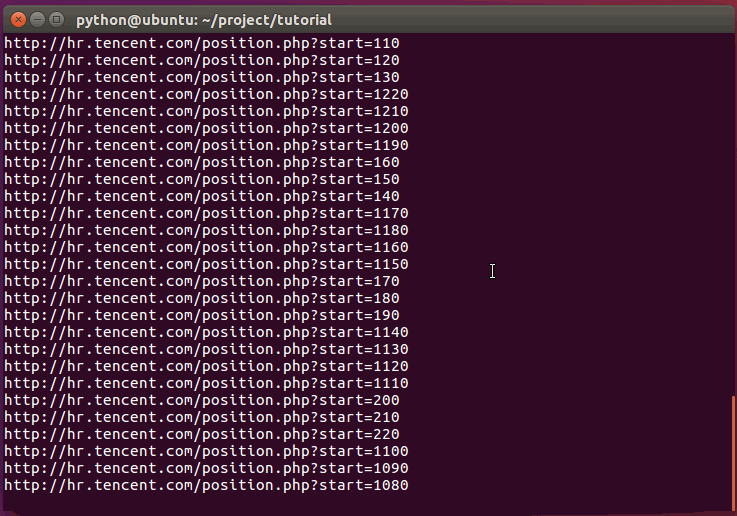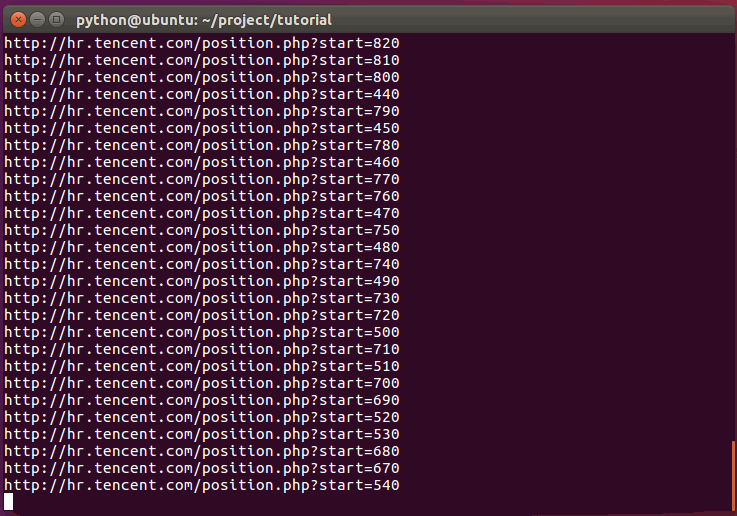
print url
yield scrapy.Request(url, callback=self.parse)
执行
scrapy crawl tencent -L INFO
CrawlSpider
scrapy.spiders.CrawlSpider
爬取一般网站常用的spider。
其定义了一些规则(rule)来提供跟进link的方便的机制。
除了从Spider继承过来的(您必须提供的)属性外(name、allow_domains),其提供了一个新的属性:
rules
包含一个(或多个) 规则对象的集合(list)。 每个Rule对爬取网站的动作定义了特定操作。 如果多个rule匹配了相同的链接,则根据规则在本集合中被定义的顺序,第一个会被使用。
parse_start_url(response)
当start_url的请求返回时,该方法被调用
爬取规则(Crawling rules)
class scrapy.contrib.spiders.Rule(link_extractor, callback=None, cb_kwargs=None, follow=None, process_links=None, process_request=None)
link_extractor:其定义了如何从爬取到的页面中提取链接。
callback:指定spider中哪个函数将会被调用。 从link_extractor中每获取到链接时将会调用该函数。该回调函数接受一个response作为其第一个参数
注意: 当编写爬虫规则时,请避免使用parse作为回调函数。由于CrawlSpider使用parse方法来实现其逻辑,如果您覆盖了 parse方法,crawl spider将会运行失败。cb_kwargs:包含传递给回调函数的参数(keyword argument)的字典。
follow:是一个布尔(boolean)值,指定了根据该规则从response提取的链接是否需要跟进。 如果callback为None,follow默认设置为True ,否则默认为False。
process_links:指定该spider中哪个的函数将会被调用,从link_extractor中获取到链接列表时将会调用该函数。该方法常用于过滤参数
process_request:指定该spider中哪个的函数将会被调用,该规则提取到每个request时都会调用该函数 (用来过滤request)
CrawlSpider案例
还是以腾讯招聘为例,给出配合rule使用CrawlSpider的例子:
首先运行
scrapy shell "http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
导入匹配规则:
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
page_lx = LinkExtractor(allow=('position.php?&start=\d+'))
查询匹配结果:
page_lx.extract_links(response)
没有查到:
page_lx = LinkExtractor(allow=(r'position\.php\?&start=\d+'))
page_lx.extract_links(response)
[Link(url='http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?start=10', text='2', fragment='', nofollow=False),
Link(url='http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?start=20', text='3', fragment='', nofollow=False),
Link(url='http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?start=30', text='4', fragment='', nofollow=False),
Link(url='http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?start=40', text='5', fragment='', nofollow=False),
Link(url='http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?start=50', text='6', fragment='', nofollow=False),
Link(url='http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?start=60', text='7', fragment='', nofollow=False),
Link(url='http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?start=70', text='...', fragment='', nofollow=False),
Link(url='http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?start=1300', text='131', fragment='', nofollow=False)]
len(page_lx.extract_links(response))
那么,scrapy shell测试完成之后,修改以下代码
#提取匹配 'http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=\d+'的链接
page_lx = LinkExtractor(allow=('start=\d+'))
rules = [
#提取匹配,并使用spider的parse方法进行分析;并跟进链接(没有callback意味着follow默认为True)
Rule(page_lx, callback='parse',follow=True)
]
这么写对吗?
callback 千万不能写parse,一定运行有错误!!
保存以下代码为tencent_crawl.py
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
from tutorial.items import RecruitItem
from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
class RecruitSpider(CrawlSpider):
name = "tencent_crawl"
allowed_domains = ["hr.tencent.com"]
start_urls = [
"http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
]
#提取匹配 'http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=\d+'的链接
page_lx = LinkExtractor(allow=('start=\d+'))
rules = [
#提取匹配,并使用spider的parse方法进行分析;并跟进链接(没有callback意味着follow默认为True)
Rule(page_lx, callback='parseContent',follow=True)
]
def parseContent(self, response):
print response.url
for sel in response.xpath('//*[@class="even"]'):
name = sel.xpath('./td[1]/a/text()').extract()[0]
detailLink = sel.xpath('./td[1]/a/@href').extract()[0]
catalog =None
if sel.xpath('./td[2]/text()'):
catalog = sel.xpath('./td[2]/text()').extract()[0]
recruitNumber = sel.xpath('./td[3]/text()').extract()[0]
workLocation = sel.xpath('./td[4]/text()').extract()[0]
publishTime = sel.xpath('./td[5]/text()').extract()[0]
#print name, detailLink, catalog,recruitNumber,workLocation,publishTime
item = RecruitItem()
item['name']=name.encode('utf-8')
item['detailLink']=detailLink.encode('utf-8')
if catalog:
item['catalog']=catalog.encode('utf-8')
item['recruitNumber']=recruitNumber.encode('utf-8')
item['workLocation']=workLocation.encode('utf-8')
item['publishTime']=publishTime.encode('utf-8')
yield item
可以修改配置文件settings.py,添加
LOG_LEVEL='INFO'
运行scrapy crawl tencent_crawl
process_links参数:动态网页爬取,动态url的处理
在爬取 https://bitsharestalk.org 的时候,发现网站会为每一个url增加一个sessionid属性,可能是为了标记用户访问历史,而且这个seesionid随着每次访问都会动态变化,这就为爬虫的去重处理(即标记已经爬取过的网站)和提取规则增加了难度。
比如 https://bitsharestalk.org/index.php?board=5.0 会变成 https://bitsharestalk.org/index.phpPHPSESSID=9771d42640ab3c89eb77e8bd9e220b53&board=5.0,下面介绍集中处理方法
仅适用你的爬虫使用的是 scrapy.contrib.spiders.CrawlSpider, 在这个内置爬虫中,你提取url要通过Rule类来进行提取,其自带了对提取后的url进行加工的函数。
rules = (
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow = ( "https://bitsharestalk\.org/index\.php\?PHPSESSID\S*board=\d+\.\d+$", "https://bitsharestalk\.org/index\.php\?board=\d+\.\d+$" )), process_links = 'link_filtering' ), #默认函数process_links
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow = ( " https://bitsharestalk\.org/index\.php\?PHPSESSID\S*topic=\d+\.\d+$" , "https://bitsharestalk\.org/index\.php\?topic=\d+\.\d+$", ),),
callback = "extractPost" ,
follow = True, process_links = 'link_filtering' ),
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow = ( "https://bitsharestalk\.org/index\.php\?PHPSESSID\S*action=profile;u=\d+$" , "https://bitsharestalk\.org/index\.php\?action=profile;u=\d+$" , ),),
callback = "extractUser", process_links = 'link_filtering' )
)
def link_filtering(self, links):
ret = []
for link in links:
url = link.url
# print "This is the yuanlai ", link.url
urlfirst, urllast = url.split( " ? " )
if urllast:
link.url = urlfirst + " ? " + urllast.split( " & " , 1)[1]
# print link.url
return links
link_filtering()函数对url进行了处理,过滤掉了sessid,关于Rule类的process_links函数和links类,官方文档中并没有给出介绍,给出一个参考 https://groups.google.com/forum/#!topic/scrapy-users/RHGtm_2GO1M(也许需要梯子,你懂得)
如果你是自己实现的爬虫,那么url的处理更是可定制的,只需要自己处理一下就可以了。
process_request参数:修改请求参数
class WeiboSpider(CrawlSpider):
name = 'weibo'
allowed_domains = ['weibo.com']
start_urls = ['http://www.weibo.com/u/1876296184'] # 不加www,则匹配不到cookie, get_login_cookie()方法正则代完善
rules = (
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'^http:\/\/(www\.)?weibo.com/[a-z]/.*'), # 微博个人页面的规则,或/u/或/n/后面跟一串数字
process_request='process_request',
callback='parse_item', follow=True), )
cookies = None
def process_request(self, request):
link=request.url
page = re.search('page=\d*', link).group()
type = re.search('type=\d+', link).group()
newrequest = request.replace(cookies =self.cookies, url='.../questionType?' + page + "&" + type)
return newrequest